Vacuum evaporation
Vacuum evaporation
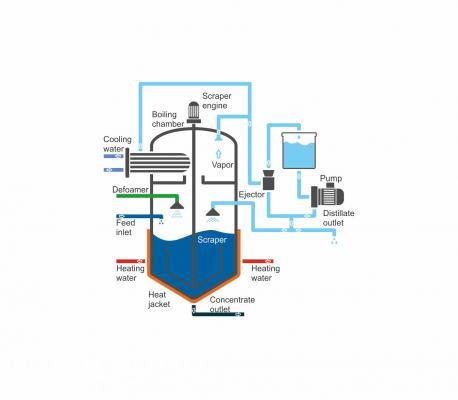
Vacuum evaporation is used to increase concentration of substances dissolved in water. Process is based on dependency of boiling temperature of water on air pressure. As opose to clasical distillation, the air pressure in boiling chamber si decreased. This means, that boiling temperature of water is also reduced. Lower boiling temperature requires less energy for heating. That’s why operating costs are very low. Vacuum evaporation has two outputs. The first one is a distillate, clean water, which can be either discharged or recycled back into the production process. The distillate has very low conductivity.
The second output is a concentrate, concentrated solution. The concentrate can be further used if it is a product or it contains valuable substances. If the concentrate is further unusable, it must be proffesionally disposed. Vacuum evaporation can achieve over 90 % volume reduction of waste water. Therefore vacuum evaporators are necessity in Zero Liquid Discharge systems for water recycling in production process. There aren’t required any additive chemicals in vacuum evaporation, which is another reason why vacuum evaporators are very eco-friendly. Automatic 24/7 operation makes evaporators easy to use and maintain.
You can find more about vacuum evaporation on dedicated website AQUADEST.CZ
Go to AQUADEST.CZ
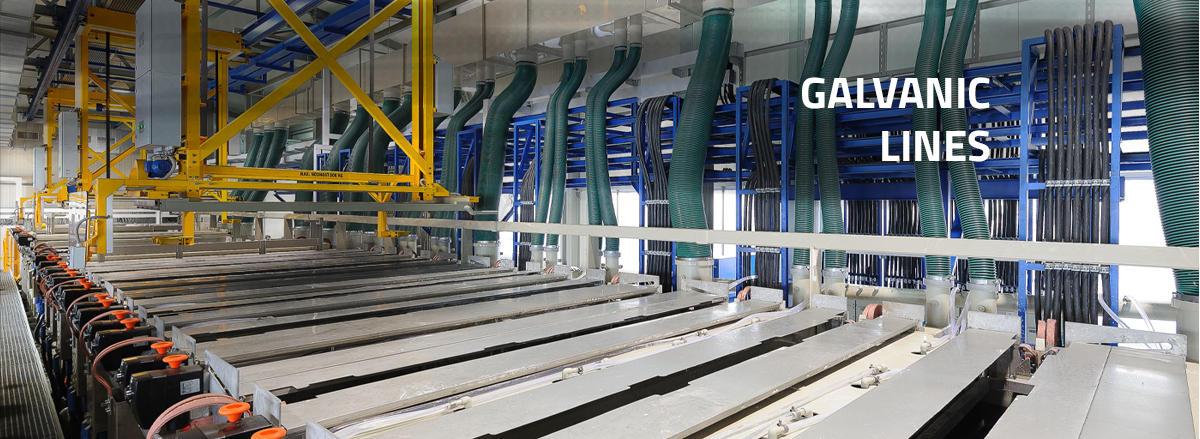
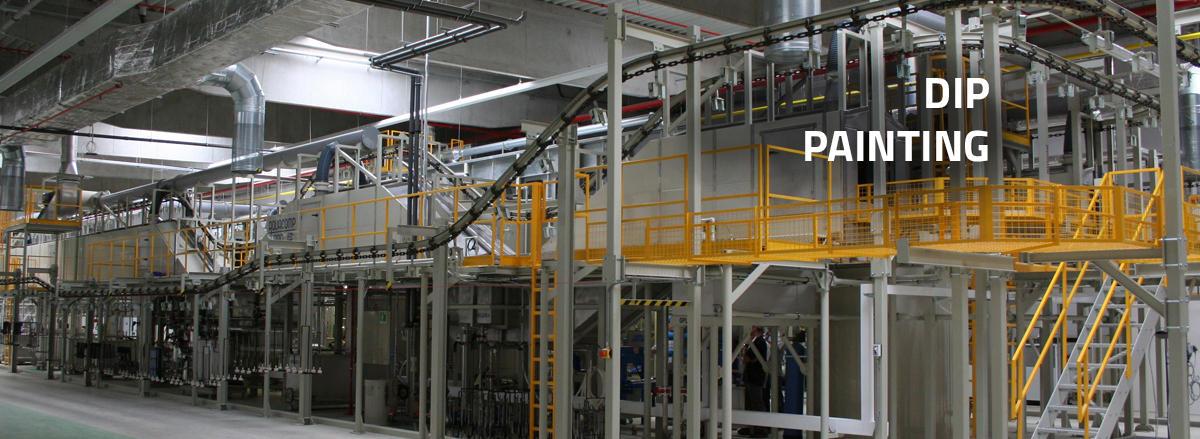
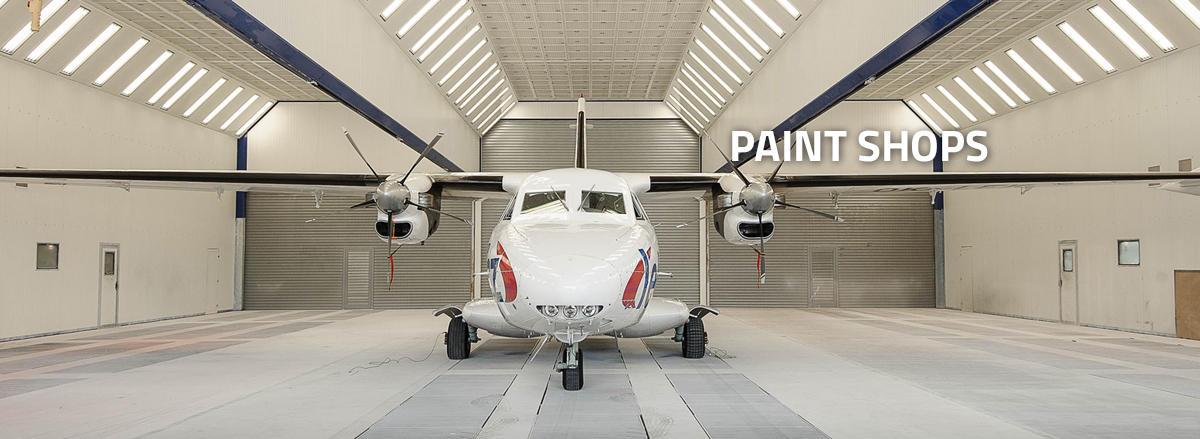
Vacuum evaporators are mainly used in:
- Chemical industry
- Surface treatment
- Machining industry
- Metallurgy
- Food industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Photographic industry
- Landfills
Areas of vacuum evaporators application:
- wastewater from die casting
- machining and other emulsions
- wastewater from vibro finishing (tumbling)
- rinse water after hardening in salt baths
- baths and rinse water from degreasing
- baths and rinse water from surface treatment
- exhausted developers and fixers
- reactors, mixers and tanks washing water
- landfill leachate
- eluates from regeneration of ion exchangers
- concentrates from membrane separation processes (reverse osmosis, ultra- a microfiltration)
Classical evaporators
|
|
|
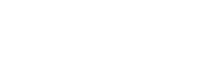
AQUADEST - K Vacuum evaporator with a heat pump AQUADEST - K can be made in following performances:
operational pressure 6 - 7 kPa |
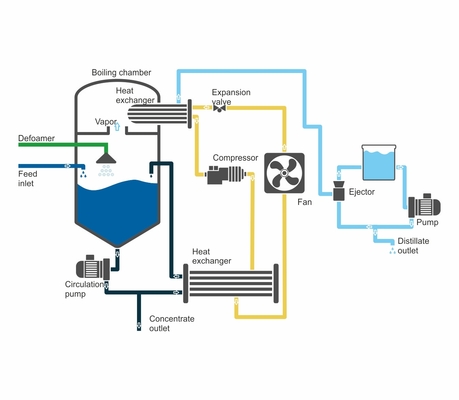
AQUADEST - D Vacuum evaporator with mechanical vapor recompresion heating system AQUADEST - D can be made in following performances:
operational pressure 70 kPa |
Crystallization evaporators
|
|
|
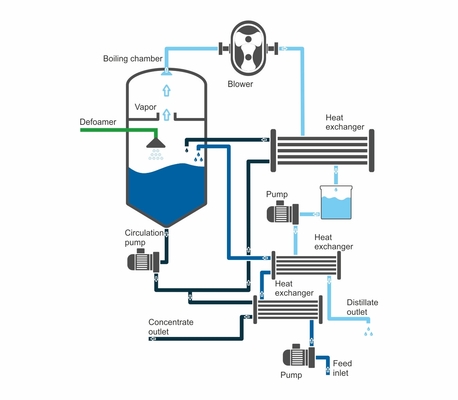
AQUADEST - KR Crystalization vacuum evaporator with heat pump AQUADEST - KR can be made in following performances:
operational pressure 6 - 7 kPa |
AQUADEST - VR Crystalization vacuum evaporator with external heat supply AQUADEST - VR can be made in following performances:
operational pressure 6 - 30 kPa |